Whoever impregnated Angela Rayner and caused her to drop out of school at the tender age of 16 with no qualifications might be disappointed that we aren’t asking who her baba mtoto (child’s father) is; whether he became a president, king or a vagabond somewhere, since the girl ‘whose leg he broke’ is now UK’s second most powerful person, 28 years since he ‘stole her goat’.
Angela’s rise to such heights after the adversity should be a lesson to countries which, six decades after independence, still have millions of citizens wallowing in poverty and denied basic human dignity, while the elite shamelessly flaunt obscene luxury on their hungry, twisted faces.
After independence, African countries also suffered their adolescent setbacks in the form of military coups. Uganda’s military rule lasted eight years, Kenya’s about eight hours on August 1, 1982, while Tanzania’s didn’t materialise and its first defence chief became an ambassador somewhere.
What we learn from Angela Rayner is that when you’re derailed, it doesn’t matter who derailed you, because nobody wants to know. What matters is that you pick yourself up, not just to march on, but to stand up and shine.To incessantly blame our colonial and slave-trading ‘derailers’ while we treat our fellow citizens worse than the colonialists did only invites the world to laugh. Have you ever read of a colonial officer demanding a bribe from a local before providing the service due?
African countries today need to press ‘reset’. A state operates by written policies, plans, strategies and prescribed penalties with gazetted prisons for those who break the rules. This is far more power than teenage Angela had, so a reset state should take less time to become prosperous than the 28 years it took her to get to the top after derailing.
So it’s realistic for countries to operate on five-year planning and electoral cycles, so a state that fails to implement a programme in five years has something wrong with it. It needs a reset.
A basic reset course for African leaders and economists should include:
1. Mindset change: Albert Einstein teaches us that no problem can be solved from the same level of consciousness that created it. For example, if you are in debt, seeking or accepting more debt is using the same level of thinking that put you there. If you don’t like Einstein’s genius, you can even try an animal in the bush that falls into a hole and stops digging. Our economists are certainly better than a beast in the bush.
2. Stealing is wrong: African leaders and civil servants need to revisit their catechism or madarasa – stealing public resources is as immoral as rape.
3. Justifying wrong doesn’t make it right: Using legalese and putting sinful benefits in the budget is immoral and can incite the deprived to destroy everything.
4. Take inventory of your resources and plan to use them: If Kenya, for example, has a railway line running from Mombasa to Nairobi, is it prudent to borrow $3.6 billion to build a highway parallel to it before paying off and electrifying the railway?
If Uganda is groaning under a $2 billion annual petrol import bill, does it make sense to beg Kenya for access to import more fuel, when Kampala is already manufacturing and marketing electric buses, while failing to use hundreds of megawatts it generates, yet the country has to pay for the unused power?
If Tanzania… okay, TZ has entered the 21st Century with its electric trains soon to be operating between Dar es Salaam and Morogoro. Ethiopia, too, has connected Addis Ababa to the port of Djibouti with a 753-kilometre electric railway, and moves hundreds of thousands of passengers in Addis every day by electric train.
5. Protect the environment: We don’t own it, we borrowed it from our parents to preserve it for our children. Who doesn’t know that the future of the planet is at stake?
6. Do monitoring and evaluation: Otherwise you may keep doing the same thing that does not work and hope for better results, as a sage defined lunacy.
7. Don’t blame the victims of your incompetence: This is basic fairness.
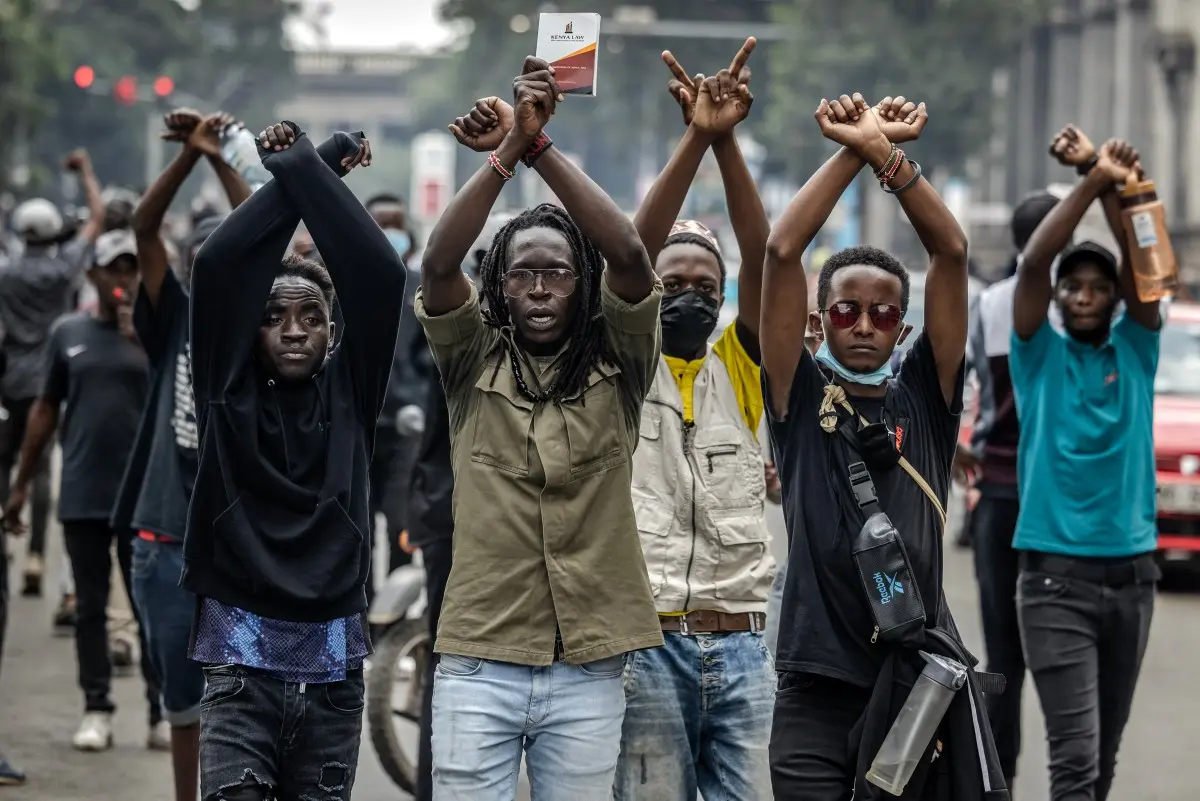
We could go on, but how boring! Who doesn’t know these mundane points? We are not holding our breath for Angela’s performance, because if she fails, she will be easily replaced. Africa’s eyes should now be on Kenya to see how they manage an abrupt change without the mass bloodshed that often accompanies revolutions.

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day ago
 Metro1 day ago
Metro1 day ago
 Metro14 hours ago
Metro14 hours ago
 Tech1 day ago
Tech1 day ago