Kenya has restarted internal consultations on the East African political federation, a pet project of leaders like Uganda’s President Yoweri Museveni, that many people like to discuss because they don’t plan to do anything about it.
There is a twist to it this time. During its stakeholder’s consultation launch, Kenya’s East African Community Cabinet Secretary Rebecca Miano said they are targeting a confederation and hoping that the EAC can start with that and then move on to a federation.
It is like you are in Nairobi and want to drive to Kampala. However, instead of heading there through either Busia or Malaba, you go via the Tanzania-Kenya border of Namanga, drive down to Dar es Salaam, then up to Dodoma, Tabora, Mwanza, the Uganda-Tanzania border of Mutukula, on to Mbarara, Masaka, and eventually Kampala.
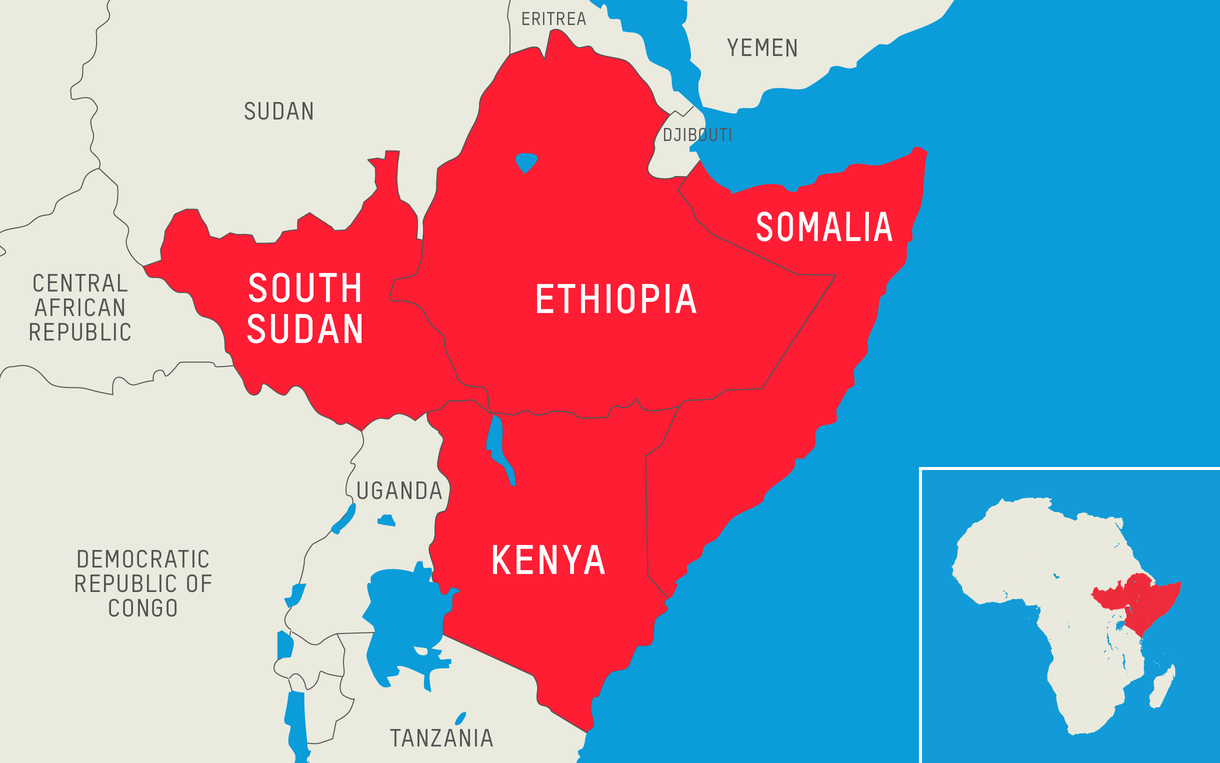
You will still get to Kampala, but you will be worse for wear and tear, have spent many long days on the road, and need to buy a new back. The dictionary tells us that a confederation is a political arrangement where the federal government (the EAC) is accountable to the member states (DRC, Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, South Sudan, Tanzania, and Uganda) who are the ultimate authority – i.e., a slight upgrade of the current situation.
The federal government holds the ultimate power in a federation, and the member states will be subordinate to it. The presidents would be like Kenya’s County Governors in the country’s devolved system, and the First Big Man/Woman will be sitting in Arusha.
Many forces have hobbled the East African Federation. There is a widespread belief that President Museveni, its most vocal supporter at the State House level, wants it for himself as a retirement gift. He would take over the job as the EAC Federation president after he’s done his 45 years in Uganda’s State House. In Kenya, especially, that terrifies too many people. It’s likely that other East African capitals, too, are waiting for a post-Museveni Uganda to emerge before they can jump seriously on the federation wagon.
But it’s mostly the national capitalists, the political class, and land nativists who are afraid of a political federation, much the same way some of them have been lukewarm to the current EAC project. They fear losing their national monopolies to other competitors and the privileges and power that border and customs controls, immigration, and local rents provide. And, in Tanzania, a deep suspicion about other East Africans being hungry wolves waiting to steal its vast lands still runs high.
Easier path
Miano, however, mentioned something that might provide an easier path to an East African federation. She said, “We now have in place the Customs Union Protocol, the EAC Common Market Protocol and the Monetary Union Protocol” (the monetary union has been problematic with countries haggling over the hosting of a regional central bank, The EastAfrican helpfully noted).
“Besides the scaffolding of our political federation, we have made significant progress in our shared economic and sociocultural cooperation and productive and services sectors, and more recently, we have enhanced cooperation in defence and interstate security,” said Miano.
The East African political federation has probably already started as a military union. An evolving “East African NATO”. East Africa has the Eastern Africa Standby Force, a regional military organisation whose job is to ensure peace and security in the Eastern African region. It is one of the five regional Forces of the African Standby Force (ASF).
East Africans have always found it easier to soldier things together – like the now-all but doomed East Africa Response Force (EARF) to eastern DRC. By contrast, you cannot get East African bankers to agree on anything, and Ugandan eggs and powdered milk tend to bring out a lot of opposition from Kenyan officialdom. If you put East African customs and tax chiefs in a room and leave them to discuss dissolving and forming a single revenue authority, you will return to find only dead bodies on the floor.
Yet, anyone who visited the African Union Mission in Somalia (Amisom) in the tough old days as it broke al Shabaab’s back in Mogadishu, and before it was recently rebaptised the AU Transitional Mission in Somalia (ATMIS), would have been struck by the camaraderie of the Ugandan, Burundian, and Kenyan officers and troops in their vast headquarters compound. For but the national flags on their uniforms, a non-East African couldn’t tell them apart. Amisom was essentially an East African military project.
In South Sudan, the Uganda People’s Defence Force (UPDF) intervened in December 2013 to save President Salva Kiir’s bacon and is still the invisible hand behind his throne. On the UN peacekeeping side, Rwanda has been a defining force. East African armies have also rubbed shoulders for long in the much-maligned UN Stabilisation Mission in the DRC, Monusco.
Joint soldiering is probably easier because there is no money lost. No Kenyan hotel manager is taking a Ugandan’s job in Kampala, or Ugandan farm produce outcompeting Kenya’s in Nairobi markets.
It might be a good idea to use Somalia as a guinea pig. Admit it into the EAC, but it joins with the Uganda, Burundi, and Kenya elements of ATMIS as its national army. Then in DRC, disarm all militias, and turn EAC forces into the national army. This arrangement will also help advance free and democratic societies in the region. A soldier who isn’t, to use the trope, “from a rival tribe,” is less likely to oppress you.
Charles Onyango-Obbo is a journalist, writer, and curator of the «Wall of Great Africans». Twitter@cobbo3

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day ago
 Metro2 days ago
Metro2 days ago
 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days ago
 Metro16 hours ago
Metro16 hours ago