Strictly Personal
The post-budget crisis in Kenya might be good for Africa, after all, By Joachim Buwembo
Published
5 months agoon
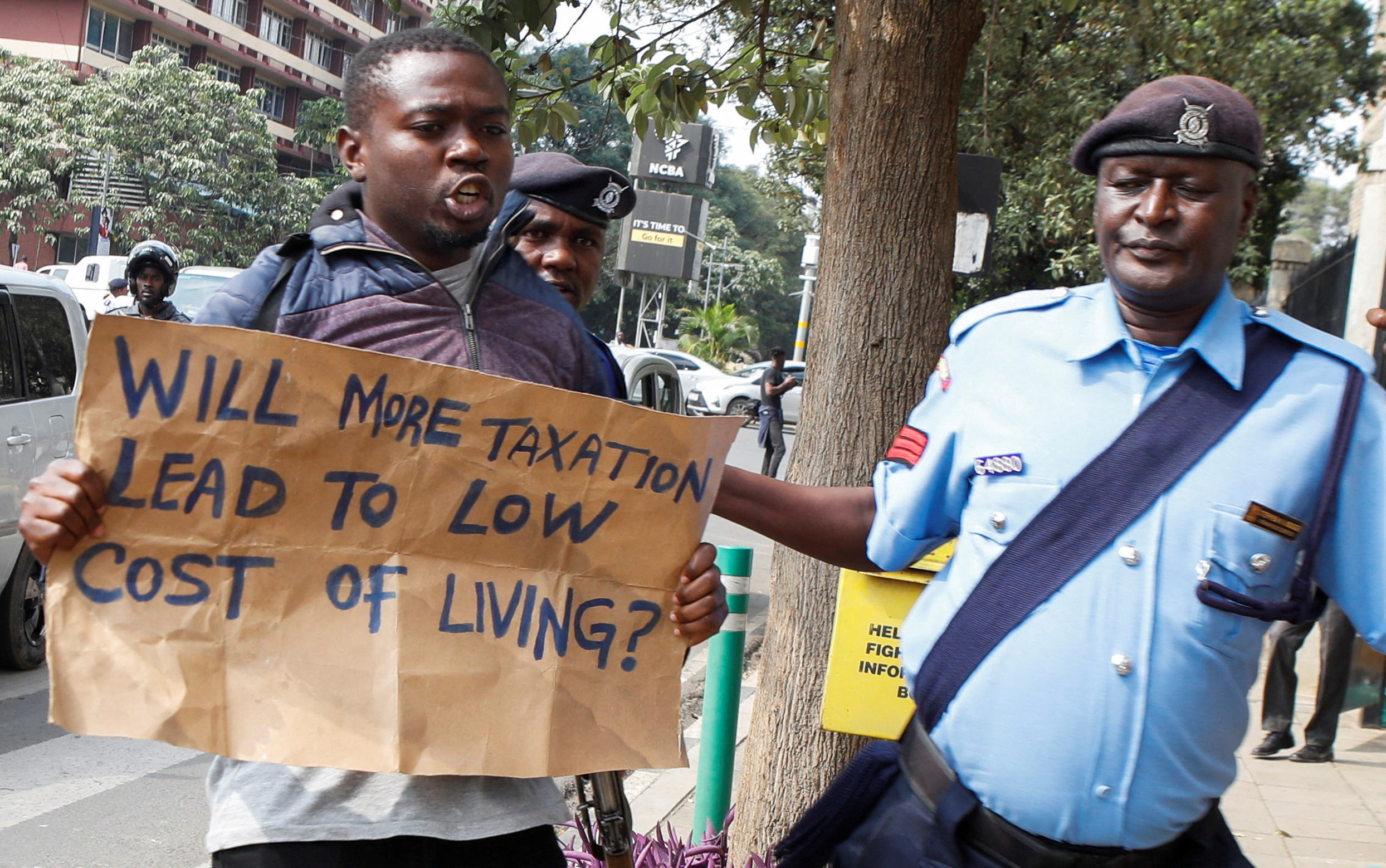
The surging crisis that is being witnessed in Kenya could end up being a good thing for Africa if the regional leaders could step back and examine the situation clinically with cool-headed interest. Maybe there is a hand of God in the whole affair. For, how do explain the flare not having started in harder-pressed countries such as Zambia, Mozambique and Ghana?
As fate would have it, it happened in East Africa, the region that is supposed to provide the next leadership of the African Union Commission, in a process that is about to start. And, what is the most serious crisis looming on Africa’s horizon? It is Debt of course.
Even the UN has warned the entire world that Africa’s debt situation is now a crisis. As at now, three or four countries are not facing debt trouble — and that is only for now.
There is one country, though, that is virtually debt-free, having just been freed from debt due to circumstances: Somalia. And it is the newest member of the East African Community. Somalia has recently had virtually all its foreign debt written off in recognition of the challenges it has been facing in nearly four decades.
Why is this important? Because debt is the choicest weapon of neocolonialists. There is no sweeter way to steal wealth than to have its owners deliver it to you, begging you, on all fours, to take it away from them, as you quietly thank the devil, who has impaired their judgement to think that you are their saviour.
So?
So, the economic integration Africa has embarked on will, over the next five or so years, go through are a make-or-break stage, and it must be led by a member that is debt-free. For, there is no surer weapon to subjugate and control a society than through debt.
A government or a country’s political leadership can talk tough and big until their creditor whispers something then the lion suddenly becomes a sheep. Positions agreed on earlier with comrades are sheepishly abandoned. Scheduled official trips get inexplicably cancelled.
Debt is that bad. In African capitals, presidents have received calls from Washington, Paris or London to cancel trips and they did, so because of debt vulnerability.
In our villages, men have lost wives to guys they hate most because of debt. At the state level, governments have lost command over their own institutions because of debt. The management of Africa’s economic transition, as may be agreed upon jointly by the continental leaders, needs to be implemented by a member without crippling foreign debt so they do not get instructions from elsewhere.
The other related threat to African states is armed conflict, often internal and not interstate. Somalia has been going through this for decades and it is to the credit of African intervention that statehood was restored to the country.
This is the biggest prize Africa has won since it defeated colonialism in (mostly) the 1960s decade. The product is the new Somalia and, to restore all other countries’ hope, the newly restored state should play a lead role in spreading stability and confidence across Africa.
One day, South Sudan, too, should qualify to play a lead role on the continent.
What has been happening in Kenya can happen in any other African country. And it can be worse. We have seen once promising countries with strong economies and armies, such as Libya, being ravaged into near-Stone Age in a very short time. Angry, youthful energy can be destructive, and opportunistic neocolonialists can make it inadvertently facilitate their intentions.
Containing prolonged or repetitive civil uprisings can be economically draining, both directly in deploying security forces and also by paralysing economic activity.
African countries also need to become one another’s economic insurance. By jointly managing trade routes with their transport infrastructure, energy sources and electricity distribution grids, and generally pursuing coordinated industrialisation strategies in observance of regional and national comparative advantages, they will sooner than later reduce insecurity, even as the borders remain porous.
You may like
-


Kenya’s startup BuuPass partners with GiftPesa to launch digital travel vouchers
-


Ugandan opposition politician abducted, wife says
-


Kenya seeks $750m from World Bank, obtains $200m from AfDB— Official
-


Kenyan marathon legend Kipchoge advises young athletes to prioritize success over money
-


Telegram faces shutdown in Kenya
-


Kenyan fintech Chumz expands into Rwanda after hitting 200k users
Strictly Personal
Budgets, budgeting and budget financing, By Sheriffdeen A. Tella, Ph.D.
Published
3 days agoon
November 20, 2024
The budget season is here again. It is an institutional and desirable annual ritual. Revenue collection and spending at the federal, State and local government levels must be authorised and guided by law. That is what budget is all about. A document containing the estimates of projected revenues from identified sources and the proposed expenditure for different sectors in the appropriate level of government. The last two weeks have seen the delivery of budget drafts to various Houses of Assembly and the promise that the federal government would present its draft budget to the National Assembly.
Do people still look forward to the budget presentation and the contents therein? I am not sure. Citizens have realised that these days, governments often spend money without reference to the approved budget. A governor can just wake up and direct that a police station be built in a location. With no allocation in the budget, the station will be completed in three months. The President can direct from his bathroom that 72 trailers of maize be distributed to the 36 states as palliatives. No budget provision, and no discussion by relevant committee or group.
We still operate with the military mentality. We operated too long under the military and of the five Presidents we have in this democracy, two of them were retired military Heads of State. Between them, they spent 16 years of 25 years of democratic governance. Hopefully, we are done with them physically but not mentally. Most present governors grew up largely under military regimes with the command system. That is why some see themselves as emperor and act accordingly. Their direct staff and commissioners are “Yes” men and women. There is need for disorientation.
The importance of budget in the art of governance cannot be overemphasized. It is one of the major functions of the legislature because without the consideration and authorisation of spending of funds by this arm of government, the executive has no power to start spending money. There is what we refer to as a budget cycle or stages. The budget drafting stage within the purview of the executive arm is the first stage and, followed by the authorisation stage where the legislature discusses, evaluates and tinkers with the draft for approval before presenting it to the President for his signature.
Thereafter, the budget enters the execution phase or cycle where programmes and projects are executed by the executive arm with the legislature carrying out oversight functions. Finally, we enter the auditing phase when the federal and State Auditors verify and report on the execution of the budgets. The report would normally be submitted to the Legislature. Many Auditor Generals have fallen victim at this stage for daring to query the executives on some aspects of the execution in their reports.
A new budget should contain the objectives and achievements of the preceding budget in the introduction as the foundation for the budget. More appropriately, a current budget derives its strength from a medium-term framework which also derives its strength from a national Development Plan or a State Plan. An approved National Plan does not exist currently, although the Plan launched by the Muhammadu Buhari administration is in the cooler. President Tinubu, who is acclaimed to be the architect of the Lagos State long-term Plan seems curiously, disillusioned with a national Plan.
Some States like Oyo and Kaduna, have long-term Plans that serve as the source of their annual budgets. Economists and policymakers see development plans as instruments of salvation for developing countries. Mike Obadan, the former Director General of the moribund Nigeria Centre for Economic and Management Administration, opined that a Plan in a developing country serves as an instrument to eradicate poverty, achieve high rates of economic growth and promote economic and social development.
The Nigerian development plans were on course until the adoption of the World Bank/IMF-inspired Structural Adjustment Programme in 1986 when the country and others that adopted the programme were forced to abandon such plan for short-term stabilisation policies in the name of a rolling plan. We have been rolling in the mud since that time. One is not surprised that the Tinubu administration is not looking at the Buhari Development Plan since the government is World Bank/IMF compliant. It was in the news last week that our President is an American asset and by extension, Nigeria’s policies must be defined by America which controls the Bretton Woods institutions.
A national Plan allows the citizens to monitor quantitatively, the projects and programmes being executed or to be executed by the government through the budgeting procedure. It is part of the definitive measures of transparency and accountability which most Nigerian governments do not cherish. So, you cannot pin your government down to anything.
Budgets these days hardly contain budget performance in terms of revenue, expenditure and other achievements like several schools, hospitals, small-scale enterprises, etc, that the government got involved in successfully and partially. These are the foundation for a new budget like items brought forward in accounting documents. The new budget should state the new reforms or transformations that would be taking place. Reforms like shifting from dominance of recurrent expenditure to capital expenditure; moving from the provision of basic needs programmes to industrialisation, and from reliance on foreign loans to dependence on domestic fund mobilisation for executing the budget.
That brings us to the issue of budget deficit and borrowing. When an economy is in recession, expansionary fiscal policy is recommended. That is, the government will need to spend more than it receives to pump prime the economy. If this is taken, Nigeria has always had a deficit budget, implying that we are always in economic recession. The fact is that even when we had a surplus in our balance of payment that made it possible to pay off our debts, we still had a deficit budget. We are so used to borrowing at the national level that stopping it will look like the collapse of the Nigerian state. The States have also followed the trend. Ordinarily, since States are largely dependent on the federal government for funds, they should promote balanced budget.
The States are like a schoolboy who depends on his parents for school fees and feeding allowance but goes about borrowing from classmates. Definitely, it is the parents that will surely pay the debt. The debt forgiveness mentality plays a major role in the process. Having enjoyed debt forgiveness in the past, the federal government is always in the credit market and does not caution the State governments in participating in the market. Our Presidents don’t feel ashamed when they are begging for debt forgiveness in international forum where issues on global development are being discussed. Not less than twice I have watched the countenance of some Presidents, even from Africa, while they looked at our president with disdain when issues of debt forgiveness for African countries was raised.
In most cases, the government, both at the federal and state cannot show the product of loans, except those lent by institutions like the World Bank or African Development Bank for specific projects which are monitored by the lending institutions. In other cases, the loans are stolen and transferred abroad while we are paying the loans. In some other cases, the loans are diverted to projects other than what the proposal stated. There was a case of loans obtained based on establishing an international car park in the border of the State but diverted to finance the election of a politician in the State. The politician eventually lost the election but the citizens of the State have to be taxed to pay the loan. Somebody as “Nigeria we hail thee”.
Transformation in budgeting should commence subsequently at the State and federal level. Now that local government will enjoy some financial autonomy and therefore budgeting process, they should be legally barred from contracting foreign loans. They have no business participating in the market. They should promote balanced budget where proposed expenditures must equal the expected revenues from federal and internal sources. The State government that cannot mobilise, from records, up to 40 percent of its total budget from IGR should not be supported to contract foreign loans. The States should engage in a balanced budget. The federal government budget should shift away from huge allocations to recurrent expenditure towards capital expenditure for capital formation and within the context of a welfarist state.
Sheriffdeen A. Tella, Ph.D.
Strictly Personal
African Union must ensure Sudan civilians are protected, By Joyce Banda
Published
4 weeks agoon
October 25, 2024
The war in Sudan presents the world – and Africa – with a test. This far, we have scored miserably. The international community has failed the people of Sudan. Collectively, we have chosen to systematically ignore and sacrifice the Sudanese people’s suffering in preference of our interests.
For 18 months, the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) have fought a pitiless conflict that has killed thousands, displaced millions, and triggered the world’s largest hunger crisis.
Crimes against humanity and war crimes have been committed by both parties to the conflict. Sexual and gender-based violence are at epidemic levels. The RSF has perpetrated a wave of ethnically motivated violence in Darfur. Starvation has been used as a weapon of war: The SAF has carried out airstrikes that deliberately target civilians and civilian infrastructure.
The plight of children is of deep concern to me. They have been killed, maimed, and forced to serve as soldiers. More than 14 million have been displaced, the world’s largest displacement of children. Millions more haven’t gone to school since the fighting broke out. Girls are at the highest risk of child marriage and gender-based violence. We are looking at a child protection crisis of frightful proportions.
In many of my international engagements, the women of Sudan have raised their concerns about the world’s non-commitment to bring about peace in Sudan.
I write with a simple message. We cannot delay any longer. The suffering cannot be allowed to continue or to become a secondary concern to the frustrating search for a political solution between the belligerents. The international community must come together and adopt urgent measures to protect Sudanese civilians.
Last month, the UN’s Independent International Fact-Finding Mission for Sudan released a report that described a horrific range of crimes committed by the RSF and SAF. The report makes for chilling reading. The UN investigators concluded that the gravity of its findings required a concerted plan to safeguard the lives of Sudanese people in the line of fire.
“Given the failure of the warring parties to spare civilians, an independent and impartial force with a mandate to safeguard civilians must be deployed without delay,” said Mohamed Chande Othman, chair of the Fact-Finding Mission and former Chief Justice of Tanzania.
We must respond to this call with urgency.
A special responsibility resides with the African Union, in particular the AU Commission, which received a request on June 21 from the AU Peace and Security Council (PSC) “to investigate and make recommendations to the PSC on practical measures to be undertaken for the protection of civilians.”
So far, we have heard nothing.
The time is now for the AU to act boldly and swiftly, even in the absence of a ceasefire, to advance robust civilian protection measures.
A physical protective presence, even one with a limited mandate, must be proposed, in line with the recommendation of the UN Fact-Finding Mission. The AU should press the parties to the conflict, particularly the Sudanese government, to invite the protective mission to enter Sudan to do its work free from interference.
The AU can recommend that the protection mission adopt targeted strategies operations, demarcated safe zones, and humanitarian corridors – to protect civilians and ensure safe, unhindered, and adequate access to humanitarian aid.
The protection mission mandate can include data gathering, monitoring, and early warning systems. It can play a role in ending the telecom blackout that has been a troubling feature of the war. The mission can support community-led efforts for self-protection, working closely with Sudan’s inspiring mutual-aid network of Emergency Response Rooms. It can engage and support localised peace efforts, contributing to community-level ceasefire and peacebuilding work.
I do not pretend that establishing a protection mission in Sudan will be easy. But the scale of Sudan’s crisis, the intransigence of the warring parties, and the clear and consistent demands from Sudanese civilians and civil society demand that we take action.
Many will be dismissive. It is true that numerous bureaucratic, institutional, and political obstacles stand in our way. But we must not be deterred.
Will we stand by as Sudan suffers mass atrocities, disease, famine, rape, mass displacement, and societal disintegration? Will we watch as the crisis in Africa’s third largest country spills outside of its borders and sets back the entire region?
Africa and the world have been given a test. I pray that we pass it.
Dr Joyce Banda is a former president of the Republic of Malawi.
EDITOR’S PICK


South African DJ Black Coffee bags World’s Best DJ 2024
South African disc jockey, DJ Black Coffee, has been named the World’s Best DJ 2024 at the Golden Moon Awards....


Wafcon 2024 draw throws up interesting pairings
The draw for the 2024 Women’s Africa Cup of Nations (Wafcon) holding in Morocco from July 5 to 26 next...


Zambian govt successfully repatriates trafficked toddler from Mozambique
The Zambian government has announced the successful repatriation of a one-year-eight-month-old child who was trafficked to Mozambique. Making the announcement...


Finland-based Nigerians in panic as authorities search for Simon Ekpa’s sponsors
Some Nigerians based in Finland have been thrown into panic mode following the arrest and detention of the self-styled Prime...


Mauritius’ Prime Minister to double as Finance Minister
In an effort to maintain a tight eye on the economy, Mauritius’ Prime Minister, Navin Ramgoolam, who took office this...


IMF mission concludes 4th loan program assessment in Egypt
Following the completion of a recent visit to Egypt, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has announced that its mission had...


Mali’s junta names spokesman Abdoulaye Maiga new Prime Minister
A day after dismissing Choguel Maiga for criticising the government, Mali’s governing junta named its spokesperson, Abdoulaye Maiga, as Prime...


Brazilian meatpacker JBS invests $2.5 billion in Nigeria, builds six facilities
Brazilian meatpacker JBS says it has inked a memorandum of understanding with the Nigerian government for a $2.5 billion investment...


China’s Xi meets with Morocco’s Crown Prince
Morocco’s official media reports that Chinese President, Xi Jinping, visited Morocco briefly on Thursday. According to Morocco’s MAP, Crown Prince...


65% of Nigerian households lack money for healthy food—Survey
A survey conducted by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) has revealed that around 65% of Nigerian households, which is...
Trending
-

 Politics1 day ago
Politics1 day agoMali’s junta names spokesman Abdoulaye Maiga new Prime Minister
-

 Metro1 day ago
Metro1 day ago65% of Nigerian households lack money for healthy food—Survey
-

 VenturesNow1 day ago
VenturesNow1 day agoIMF mission concludes 4th loan program assessment in Egypt
-

 Musings From Abroad1 day ago
Musings From Abroad1 day agoBrazilian meatpacker JBS invests $2.5 billion in Nigeria, builds six facilities


