Strictly Personal
Down memory lane when Rwanda and Burundi joined the EA party by Charles Onyango-Obbo
Published
3 years agoon
In a few days, it will be exactly 15 years since Rwanda and Burundi acceded to the East African Community Treaty on June 18, 2007.
They have been remarkable — and very long — years. In June of 2007, Kenyan telco giant Safaricom’s mobile money service M-Pesa was just a couple of weeks old, and not too many people took it seriously.
Kenya was still basking in the post-Kanu-ouster glow, and the historic opposition and democratic triumph that had brought Mwai Kibaki to power.
Six months later, Kenya was up in flames following the disputed December 2007 election, in the country’s worst post-independence bout of mass murder.
Nearly 800 people were killed in the post-election violence, but those same circumstances led to the explosion.
Today, it’s both Africa’s and the world’s leading mobile money service.
The Project Management Institute’s 2019 Most Influential Projects list recognised M-Pesa as the ninth most influential project in the world over the past 50 years, trouncing hundreds of others, including Bitcoin and Netflix’s streaming service.
In Burundi, Pierre Nkurunziza had been elected president two years earlier, and it looked like the country was poised for a dramatic recovery after more than a decade of civil war.
In the same year in March, Uganda went out on a limb and sent troops in a daring move to Somalia as the first contingent of the African Union Peacekeeping Mission in Somalia (Amisom), now the African Union Transitional Mission in Somalia (ATMIS).
Only those with a death wish entered the Somali fray those days. Months later, Burundi followed. With all the problems of Amisom, it started the process that eventually considerably altered Somalia’s fortunes.
There was peace in all the territories comprising the EAC then and today; in the Democratic Republic of Congo there was a lull after the “Second Congo War”. The M23 rebels and others were nowhere.
South Sudan was peaceful following the Nairobi-brokered Comprehensive Peace Agreement of 2005.
With the death of the charismatic John Garang, leader of the Sudan People’s Liberation Army/Movement in July 2005, the tide had turned in favour of independence.
However, optimism was so sky-high that when that new South Sudan was born, a golden era would start for it too. Mostly hell followed after that independence in 2011.
The region was embracing the world. Later, in November of 2007, the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting was held in Kampala. It returns to East Africa from June 22 to 25, in Kigali.
There had been an upswell in Africa of what seemed like a new morality in 2007, which, among other things, got Uganda and Burundi to put their troops in harm’s way in Somalia, considered then one of the world’s most intractable crises. It partly led to silencing of the guns.
It was emblematic in Nelson Mandela’s 2007 rebuke of Zimbabwean president Robert Mugabe when he asked “Uncle Bob” to resign over growing human rights abuses in his country.
When that didn’t bear fruit, he spoke out publicly against Mugabe in 2007, asking him to step down “with residual respect and a modicum of dignity.”
We’d never have imagined that 2020, 2021 and 2022 would come one day.
Charles Onyango-Obbo is a journalist, writer, and curator of the “Wall of Great Africans”. Twitter@cobbo3
You may like
-


Let’s merge EAC and Igad, By Nuur Mohamud Sheekh
-


African Union must ensure Sudan civilians are protected, By Joyce Banda
-


Economic policies must be local, By Lekan Sote
-


Dangote Refinery: A timely win for industrialisation, By Abiodun Alade
-


Mpox crisis: We need an equity-driven pandemic treaty, By Magda Robalo
-


Olympics had free lessons for African leaders, By Tee Nugugi
Strictly Personal
Let’s merge EAC and Igad, By Nuur Mohamud Sheekh
Published
3 weeks agoon
November 27, 2024
In an era of political and economic uncertainty, global crises and diminishing donor contributions, Africa’s regional economic communities (RECs) must reimagine their approach to regional integration.
The East African Community (EAC) and the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (Igad), two critical RECs in East Africa and the Horn of Africa have an unprecedented opportunity to join forces, leveraging their respective strengths to drive sustainable peace and development and advance regional economic integration and promote the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA).
Already, four of the eight Igad member states are also members of the EAC and, with Ethiopia and Sudan showing interest, the new unified bloc would be formidable.
Igad’s strength lies in regional peacemaking, preventive diplomacy, security, and resilience, especially in a region plagued by protracted conflicts, climate challenges, and humanitarian crises. The EAC, on the other hand, has made remarkable strides in economic integration, exemplified by its Customs Union, Common Market, and ongoing efforts toward a monetary union. Combining these comparative advantages would create a formidable entity capable of addressing complex challenges holistically.
Imagine a REC that pairs Igad’s conflict resolution strengths with the EAC’s diplomatic standing and robust economic framework. Member states of both are also contributing troops to peacekeeping missions. Such a fusion would streamline efforts to create a peaceful and economically prosperous region, addressing the root causes of instability while simultaneously promoting trade investment and regional cooperation.
These strengths will be harnessed to deal with inter-state tensions that we are currently witnessing, including between Ethiopia and Somalia over the Somaliland MoU, strained relations between Djibouti and Eritrea, and the continually deteriorating relations between Eritrea and Ethiopia.
The global economy experienced as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, compounded by the Ukraine war and competing global crises, has strained donor countries and reduced financial contributions to multilateral organisations and African RECs. Member states, many of which are grappling with fiscal constraints, are increasingly unable to fill this gap, failing to make timely contributions, which is in turn affecting key mandate areas of Igad and EAC, and staff morale.
A merger between Igad and EAC would alleviate this financial pressure by eliminating redundancies. Shared administrative systems, integrated programmes, and a unified leadership structure would optimise resources, enabling the new REC to achieve more with less. Staff rationalisation, while sensitive, is a necessary step to ensure that limited funds are channelled toward impactful initiatives rather than duplicative overheads.
The African Union (AU) envisions a fully integrated Africa, with RECs serving as the building blocks of the AfCFTA. A unified EAC-Igad entity would become a powerhouse for regional integration, unlocking economies of scale and harmonising policies across a wider geographical and economic landscape.
This merger would enhance the implementation of the AfCFTA by creating a larger, more cohesive market that attracts investment, fosters innovation, and increases competitiveness. By aligning trade policies, infrastructure projects, and regulatory frameworks, the new REC could serve as a model for others, accelerating continental integration.
The road to integration is not without obstacles. Political will, divergent institutional mandates, and the complexity of harmonising systems pose significant challenges. However, these hurdles are surmountable through inclusive dialogue, strong leadership, and a phased approach to integration.
Member states must prioritise the long-term benefits of unity over short-term political considerations. Civil society, the private sector, the youth, and international partners also have a critical role to play in advocating for and supporting this transformative initiative.
The time for EAC and Igad to join forces is now. By merging into a single REC, they would pool their strengths, optimise resources, and position themselves as a driving force for regional and continental integration. In doing so, they would not only secure a prosperous future for their citizens and member states but also advance the broader vision of an integrated and thriving Africa.
As the world grapples with crises, Africa must look inward, embracing the power of unity to achieve its potential. A combined Igad-EAC is the bold step forward that the continent needs.
Nuur Mohamud Sheekh, a diplomatic and geopolitical analyst based in London, is a former spokesperson of the Igad Executive Secretary. X: @NuursViews
Strictly Personal
Budgets, budgeting and budget financing, By Sheriffdeen A. Tella, Ph.D.
Published
4 weeks agoon
November 20, 2024
The budget season is here again. It is an institutional and desirable annual ritual. Revenue collection and spending at the federal, State and local government levels must be authorised and guided by law. That is what budget is all about. A document containing the estimates of projected revenues from identified sources and the proposed expenditure for different sectors in the appropriate level of government. The last two weeks have seen the delivery of budget drafts to various Houses of Assembly and the promise that the federal government would present its draft budget to the National Assembly.
Do people still look forward to the budget presentation and the contents therein? I am not sure. Citizens have realised that these days, governments often spend money without reference to the approved budget. A governor can just wake up and direct that a police station be built in a location. With no allocation in the budget, the station will be completed in three months. The President can direct from his bathroom that 72 trailers of maize be distributed to the 36 states as palliatives. No budget provision, and no discussion by relevant committee or group.
We still operate with the military mentality. We operated too long under the military and of the five Presidents we have in this democracy, two of them were retired military Heads of State. Between them, they spent 16 years of 25 years of democratic governance. Hopefully, we are done with them physically but not mentally. Most present governors grew up largely under military regimes with the command system. That is why some see themselves as emperor and act accordingly. Their direct staff and commissioners are “Yes” men and women. There is need for disorientation.
The importance of budget in the art of governance cannot be overemphasized. It is one of the major functions of the legislature because without the consideration and authorisation of spending of funds by this arm of government, the executive has no power to start spending money. There is what we refer to as a budget cycle or stages. The budget drafting stage within the purview of the executive arm is the first stage and, followed by the authorisation stage where the legislature discusses, evaluates and tinkers with the draft for approval before presenting it to the President for his signature.
Thereafter, the budget enters the execution phase or cycle where programmes and projects are executed by the executive arm with the legislature carrying out oversight functions. Finally, we enter the auditing phase when the federal and State Auditors verify and report on the execution of the budgets. The report would normally be submitted to the Legislature. Many Auditor Generals have fallen victim at this stage for daring to query the executives on some aspects of the execution in their reports.
A new budget should contain the objectives and achievements of the preceding budget in the introduction as the foundation for the budget. More appropriately, a current budget derives its strength from a medium-term framework which also derives its strength from a national Development Plan or a State Plan. An approved National Plan does not exist currently, although the Plan launched by the Muhammadu Buhari administration is in the cooler. President Tinubu, who is acclaimed to be the architect of the Lagos State long-term Plan seems curiously, disillusioned with a national Plan.
Some States like Oyo and Kaduna, have long-term Plans that serve as the source of their annual budgets. Economists and policymakers see development plans as instruments of salvation for developing countries. Mike Obadan, the former Director General of the moribund Nigeria Centre for Economic and Management Administration, opined that a Plan in a developing country serves as an instrument to eradicate poverty, achieve high rates of economic growth and promote economic and social development.
The Nigerian development plans were on course until the adoption of the World Bank/IMF-inspired Structural Adjustment Programme in 1986 when the country and others that adopted the programme were forced to abandon such plan for short-term stabilisation policies in the name of a rolling plan. We have been rolling in the mud since that time. One is not surprised that the Tinubu administration is not looking at the Buhari Development Plan since the government is World Bank/IMF compliant. It was in the news last week that our President is an American asset and by extension, Nigeria’s policies must be defined by America which controls the Bretton Woods institutions.
A national Plan allows the citizens to monitor quantitatively, the projects and programmes being executed or to be executed by the government through the budgeting procedure. It is part of the definitive measures of transparency and accountability which most Nigerian governments do not cherish. So, you cannot pin your government down to anything.
Budgets these days hardly contain budget performance in terms of revenue, expenditure and other achievements like several schools, hospitals, small-scale enterprises, etc, that the government got involved in successfully and partially. These are the foundation for a new budget like items brought forward in accounting documents. The new budget should state the new reforms or transformations that would be taking place. Reforms like shifting from dominance of recurrent expenditure to capital expenditure; moving from the provision of basic needs programmes to industrialisation, and from reliance on foreign loans to dependence on domestic fund mobilisation for executing the budget.
That brings us to the issue of budget deficit and borrowing. When an economy is in recession, expansionary fiscal policy is recommended. That is, the government will need to spend more than it receives to pump prime the economy. If this is taken, Nigeria has always had a deficit budget, implying that we are always in economic recession. The fact is that even when we had a surplus in our balance of payment that made it possible to pay off our debts, we still had a deficit budget. We are so used to borrowing at the national level that stopping it will look like the collapse of the Nigerian state. The States have also followed the trend. Ordinarily, since States are largely dependent on the federal government for funds, they should promote balanced budget.
The States are like a schoolboy who depends on his parents for school fees and feeding allowance but goes about borrowing from classmates. Definitely, it is the parents that will surely pay the debt. The debt forgiveness mentality plays a major role in the process. Having enjoyed debt forgiveness in the past, the federal government is always in the credit market and does not caution the State governments in participating in the market. Our Presidents don’t feel ashamed when they are begging for debt forgiveness in international forum where issues on global development are being discussed. Not less than twice I have watched the countenance of some Presidents, even from Africa, while they looked at our president with disdain when issues of debt forgiveness for African countries was raised.
In most cases, the government, both at the federal and state cannot show the product of loans, except those lent by institutions like the World Bank or African Development Bank for specific projects which are monitored by the lending institutions. In other cases, the loans are stolen and transferred abroad while we are paying the loans. In some other cases, the loans are diverted to projects other than what the proposal stated. There was a case of loans obtained based on establishing an international car park in the border of the State but diverted to finance the election of a politician in the State. The politician eventually lost the election but the citizens of the State have to be taxed to pay the loan. Somebody as “Nigeria we hail thee”.
Transformation in budgeting should commence subsequently at the State and federal level. Now that local government will enjoy some financial autonomy and therefore budgeting process, they should be legally barred from contracting foreign loans. They have no business participating in the market. They should promote balanced budget where proposed expenditures must equal the expected revenues from federal and internal sources. The State government that cannot mobilise, from records, up to 40 percent of its total budget from IGR should not be supported to contract foreign loans. The States should engage in a balanced budget. The federal government budget should shift away from huge allocations to recurrent expenditure towards capital expenditure for capital formation and within the context of a welfarist state.
Sheriffdeen A. Tella, Ph.D.
EDITOR’S PICK


Ghana: President-elect Mahama appoints anti-corruption team
According to a statement released by his transition team on Wednesday, Ghana’s President-elect, John Dramani Mahama, has designated an anti-corruption...
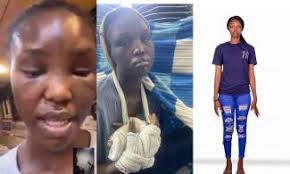

Nigerian woman trafficked to Iraq cries out for help, begs to return home
A young Nigerian lady identified as Odunayo Eniola Isaac, who is a victim of human trafficking, has cried out for...


DR Congo sues tech giant Apple over illegal mineral exploitation
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), has filed a criminal case against the European subsidiaries of tech giant, Apple, accusing...


UNESCO lists Ghana’s Kente cloth as cultural heritage
The iconic Ghanaian Kente, a piece of clothing, has been recognized as a cultural heritage on UNESCO’s Representative List of...


Zambia: FOX report highlights persistent media harassment, calls for reforms
A new Freedom of Expression (FOX) report by the Media Institute for Southern Africa (MISA) Zambia, has raised concerns over...


Egyptian court upholds ex-presidential candidate Ahmed Tantawy’s sentence
Former presidential candidate, Ahmed Tantawy, and his campaign manager, Mohamed Abou El-Diar, were found guilty of faking election paperwork, and...


Court orders Uganda to compensate LRA war crimes victims
Uganda’s tribunal has ordered the government to pay up to 10 million Ugandan shillings ($2,740) to each victim of Lord’s...


Nigeria: 614,937 killed, 2.2m abducted in 1 year— Report
A new report released on Tuesday by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) has revealed that over 614,937 Nigerians were...


Seeking to expand ties in Africa, Indonesia’s Prabowo attends D-8 economic meeting in Egypt
According to the government, Indonesian President, Prabowo Subianto, travelled to Egypt on Tuesday to attend meetings of the D-8 Organisation...


M23 Angola peace talks break down as Congo, Rwanda dash hopes
Hopes of an agreement to end Congo’s M23 rebel conflict, which has displaced over 1.9 million people, were dashed when...
Trending
-

 VenturesNow1 day ago
VenturesNow1 day agoNigeria’s November inflation rate hits 34.60%
-

 VenturesNow1 day ago
VenturesNow1 day agoIMF’s latest board reviews result in $182 million to Rwanda
-

 VenturesNow1 day ago
VenturesNow1 day agoNigeria obtains $600 million international loans for agriculture
-

 Politics1 day ago
Politics1 day agoGhana will not leave IMF but wants adjustments, says President-elect


