Strictly Personal
Inside the special mission to save Nigerian music; and why the rest of Africa should care, By Chinedu Chidi
Published
8 months agoon

When famed German composer and pianist, Beethoven described music as a “higher revelation than all wisdom and philosophy” and as “the electrical soil in which the spirit lives, thinks and invents”, he may well have laid out a profound exposition of the depth and reaches of the art, one that is unrestricted by time or distance, by creed or colour, by status or zone. He envisioned a limitless art form. Today, we speak not only of its internal freedoms, but of its transcendent liberating force coursing through entertainment, education, politics, the economy, technology, and social change. Music has become a life form meandering like the bellows of an accordion into the many circles that define life as we know it.
The conception of the MTN MUSON Music Scholars Program in 2006, a partnership between MTN Foundation and the Musical Society of Nigeria (MUSON) School of Music, was a clear reflection of a keen appreciation of this power of music. It was a visionary idea that laid a foundation that would redefine the story, not only of aspiring and practicing musicians, but of the music industry itself. Looking back, it appears a bold demonstration of faith in the promise of Nigerian music while still at comparatively modest levels, and a commensurate investment in the vehicle that would drive its actualization. Today, over 300 graduates later, the Nigerian music industry has grown in leaps and bounds. With over $2 billion in revenue annually, over 30 million monthly listeners worldwide, over 500 music producers, over 1000 record labels, over 50 radio stations amplifying its rhythms and sounds, and multiple digital music distribution platforms, Nigerian music has become the stuff of dreams, if only commercially.
The partnership involves a 2-year Diploma in Music at the MUSON Diploma School. All the students admitted to the Diploma course receive MTNF Scholarships comprising annual scholarships worth N250,000 to cover tuition, books and transportation over a 2-year period. The graduating students are awarded an internationally recognized Diploma in Music. The scholarship is an open opportunity one. It allows applications from all musically talented youth through an open and fair process.

MUSON Diploma School student performing
MTN Foundation’s investment in this educational scholarship is not an isolated endeavour; it is an integral part of the foundation’s broad commitment to promoting youth development through empowering the nation’s young people with the “skills, tools, access, knowledge, and opportunities to become economically active citizens”. The foundation combines this intervention with its “National Priority” portfolio which “focuses on Initiatives that support community infrastructure development and health-related initiatives that support women and children”. Together, the initiatives align with the objectives of the Government’s National Development plan and te UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Since its founding in 2004, the MTN Foundation has invested over N23.7 Billion in the 36 states of the federation and FCT, has over 1,017 project sites across Nigeria, with 50 unique projects spanning 3,319 communities. Overall, it has reached over 31 million people.

MTN Foundation’s Executive Director, Odunayo Sanda, (third from left) with PAU’s Director of Professional Programmes, flanked by MTN MIP Fellows
All this has been made possible by MTN Nigeria Communication PLC, its parent body, which has committed up to 1% of its Profit after Tax (PAT) to the foundation. Far-reaching strategic partnerships with key stakeholders have also been a major driver of the social investments.
MTN Foundation’s choice of MUSON School of Music was thus no coincidence. MUSON has been at the heart of developing and preserving the purest form of music in Nigeria, and helping to export same to the rest of Africa and the world. Created in 1989 by a group of friends, namely Mr. Louis Mbanefo (SAN), Mr. Akintola Williams (late), Chief Ayo Rosiji (late), Mrs. Francesca Emanuel (late) and Chief Rasheed Gbadamosi (late), the school was designed to promote, as Mr. Mbanefo, who is Chairman of the school, aptly captures, “the performance, understanding and enjoyment of serious music”. The dream, he notes, has continued to be realized, producing internationally reputed graduates and changing the dynamics of music in Nigeria and Africa. “The school has produced over 400 Diploma graduates, many of whom have continued their musical education in Europe, South Africa and America and attained international recognition. Most of our alumni have made and are making very impressive contributions to the musical life in Nigeria and indeed, the world. They have raised considerably the standard of singing and musical performance in churches, in schools and at social events. Indeed, many churches and musical societies throughout Nigeria are borrowing from the templates established by MUSON”, he proudly reveals.

The MUSON Centre, Lagos
As the proud owner of Nigeria’s “only professional Symphony Orchestra” and a choir of international renown, the school boasts a rich platform for empowering young Nigerian artistes and instrumentalists, especially in the dying art of classical and orchestral music performance.
Accredited by the Federal Government to award Diplomas in Music since 2002, the MUSON Diploma School grants all MTNF MUSON graduates diplomas which are equal to those awarded by the Associated Board of the Royal Schools of Music in the United Kingdom.

MTN Foundation graduates
Perhaps the most critical area of importance that MTN Foundation’s music intervention serves is the preservation of the fine arts of the classical, orchestral and live performance genres, with their accompanying socially valuable messaging. The rapid rise of studio-recorded music, with its massive commercial success, has sadly provided an alternative to total music, one that substantively accommodates a wide array of ‘real’ instruments, trained voice, and electrifying theatre. It is perhaps the appeal of total music that inspired Victor Hugo to bellow, “Music expresses that which cannot be put into words and that which cannot remain silent”.
This challenge is one that is not only unique to Nigeria or Africa, but a universal one. In Sasha Frere-Jones’ piece, “Do Recordings Kill Music?”, she cited a profound quote from Richard Kostelanetz’s interview with John Cage, thus: “I’ve always said that a record is not faithful to the nature of music.” David Grubbs, a professor at the Conservatory of Music at Brooklyn College, she reports, “takes up a specific belief of Cage’s: that recordings can injure the ability of an audience member to experience a performance in real time. In theoretical terms, the recording reifies a specific moment, potentially interfering with a composition’s ability to live and change and breathe by fixing a single iteration as the ‘authoritative’ version”. Perhaps, nothing captures the triumphantly seductive and absorbing force of the authentic live performance than Robert Ashley’s description of Alvin Lucier’s 1969 piece, “Vespers” as referenced by Grubbs. Ashley wrote of “Vespers”: “No number of microphones and loudspeakers can reproduce the relationship between the sounds and the space in which the sounds create the musical experience.” This reminds one of Mozart’s delicate refrain that “The music is not in the notes, but in the silence between.”
This dying art form was once the force that rocked the bowels of mother Africa, from the Sahara to the Mediterranean. From Fela and Makeba to N’Dour, Salif Keita, Amr Diab, Sangare, Mapfumo, Kidjo, Mtukudzi and Ladysmith Black Mambazo, the glory days of message-laden total music may, but for the flickers embodied by the likes of the eternal Kidjo and the heirs to the Fela dynasty, be well and truly over.
But the rebirth glistening in the hallways of MUSON Diploma School offers hope. The school is home to the award-winning MUSON Diploma Choir directed by Sir Emeka Nwokedi, and the MUSON School Orchestra & Concert Bands. It has been able to produce outstanding Jazz ensembles such as the all-female GIRLZ RULE Band, the 5YZ MEN and The Theosolites.

At MUSON, MTN Scholars take advanced training in music with majors in voice or any of the instrument forms of: Piano, Organ, Violin, Viola, Cello, Double Bass, Flute, Clarinet, Saxophone, Trumpet, Trombone, Percussion, and Classical Guitar. “Students are also required to take 2 terms of an instrument minor other than their major instrumental family. All voice students must pass grade 2 piano, instrumentalists must pass vocal techniques and all students must belong to the choir. Orchestra is required for all string majors. All wind and percussion majors must belong to band. Others who may not be majors are welcome to audition for the orchestra band”, the school says. They also take part in high-level musical productions which provide the perfect opportunity to exhibit their talents and skills. At the end of their programme, the music scholars have the opportunity to showcase the result of their advanced training through performances at the annual Donors Appreciation Concert. This speaks to the neat integration of sound and rhythm, of theatre and messaging; the total music.

If the MUSON Diploma School is to continue to plot the course for Nigeria’s music salvation and become the sure hope of total music’s triumph for all of Africa, then it must display resilience, which its parent body— The Musical Society of Nigeria— chose as its Festival of Arts theme during the celebration of its 40th anniversary earlier this year. It must be resilient in the face of the onslaught of crass commercialism. It must be defiantly resilient if it must realize its goal of producing “well-rounded, thoroughly educated musicians…comparable to those found in a Conservatoire”.
And in its resilience, it must remember that lodged in the soul of this art, in its purest form, are the currents of humanity.
You may like
-


We will handle planned nationwide protests as family matter— Nigerian Govt
-


Shelve your planned protest, I’m addressing your grievances, Tinubu begs Nigerian youths
-


Dangote Refinery in crude supply negotiations with Libya
-


Nigeria: Presidency warns against planned nationwide protest, accuses opposition
-


Meta faces $220 million fine from Nigeria for breaking consumer, data rules
-


Nigerian govt to spend N3tn on new minimum wage, pensions, gratuities— Minister
Strictly Personal
All eyes in Africa are on Kenya’s bid for a reset, By Joachim Buwembo
Published
5 days agoon
July 21, 2024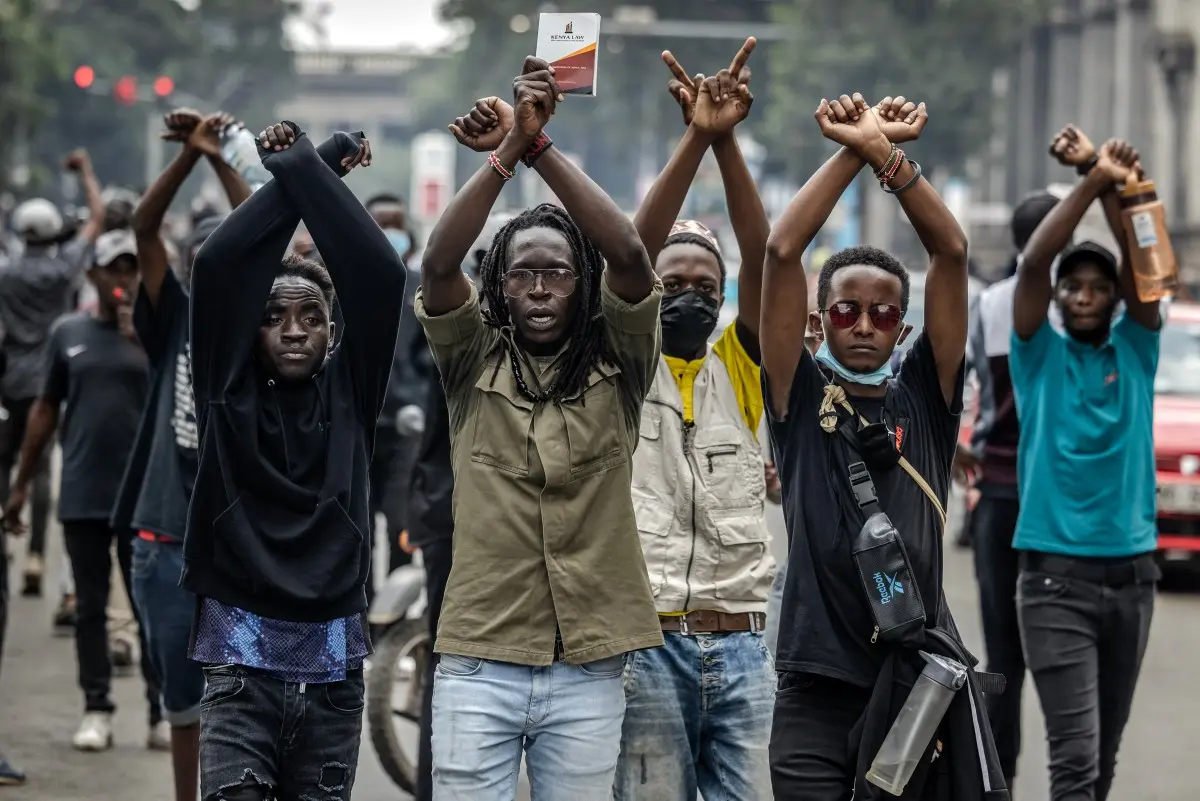
Whoever impregnated Angela Rayner and caused her to drop out of school at the tender age of 16 with no qualifications might be disappointed that we aren’t asking who her baba mtoto (child’s father) is; whether he became a president, king or a vagabond somewhere, since the girl ‘whose leg he broke’ is now UK’s second most powerful person, 28 years since he ‘stole her goat’.
Angela’s rise to such heights after the adversity should be a lesson to countries which, six decades after independence, still have millions of citizens wallowing in poverty and denied basic human dignity, while the elite shamelessly flaunt obscene luxury on their hungry, twisted faces.
After independence, African countries also suffered their adolescent setbacks in the form of military coups. Uganda’s military rule lasted eight years, Kenya’s about eight hours on August 1, 1982, while Tanzania’s didn’t materialise and its first defence chief became an ambassador somewhere.
What we learn from Angela Rayner is that when you’re derailed, it doesn’t matter who derailed you, because nobody wants to know. What matters is that you pick yourself up, not just to march on, but to stand up and shine.To incessantly blame our colonial and slave-trading ‘derailers’ while we treat our fellow citizens worse than the colonialists did only invites the world to laugh. Have you ever read of a colonial officer demanding a bribe from a local before providing the service due?
African countries today need to press ‘reset’. A state operates by written policies, plans, strategies and prescribed penalties with gazetted prisons for those who break the rules. This is far more power than teenage Angela had, so a reset state should take less time to become prosperous than the 28 years it took her to get to the top after derailing.
So it’s realistic for countries to operate on five-year planning and electoral cycles, so a state that fails to implement a programme in five years has something wrong with it. It needs a reset.
A basic reset course for African leaders and economists should include:
1. Mindset change: Albert Einstein teaches us that no problem can be solved from the same level of consciousness that created it. For example, if you are in debt, seeking or accepting more debt is using the same level of thinking that put you there. If you don’t like Einstein’s genius, you can even try an animal in the bush that falls into a hole and stops digging. Our economists are certainly better than a beast in the bush.
2. Stealing is wrong: African leaders and civil servants need to revisit their catechism or madarasa – stealing public resources is as immoral as rape.
3. Justifying wrong doesn’t make it right: Using legalese and putting sinful benefits in the budget is immoral and can incite the deprived to destroy everything.
4. Take inventory of your resources and plan to use them: If Kenya, for example, has a railway line running from Mombasa to Nairobi, is it prudent to borrow $3.6 billion to build a highway parallel to it before paying off and electrifying the railway?
If Uganda is groaning under a $2 billion annual petrol import bill, does it make sense to beg Kenya for access to import more fuel, when Kampala is already manufacturing and marketing electric buses, while failing to use hundreds of megawatts it generates, yet the country has to pay for the unused power?
If Tanzania… okay, TZ has entered the 21st Century with its electric trains soon to be operating between Dar es Salaam and Morogoro. Ethiopia, too, has connected Addis Ababa to the port of Djibouti with a 753-kilometre electric railway, and moves hundreds of thousands of passengers in Addis every day by electric train.
5. Protect the environment: We don’t own it, we borrowed it from our parents to preserve it for our children. Who doesn’t know that the future of the planet is at stake?
6. Do monitoring and evaluation: Otherwise you may keep doing the same thing that does not work and hope for better results, as a sage defined lunacy.
7. Don’t blame the victims of your incompetence: This is basic fairness.
We could go on, but how boring! Who doesn’t know these mundane points? We are not holding our breath for Angela’s performance, because if she fails, she will be easily replaced. Africa’s eyes should now be on Kenya to see how they manage an abrupt change without the mass bloodshed that often accompanies revolutions.
Strictly Personal
The post-budget crisis in Kenya might be good for Africa, after all, By Joachim Buwembo
Published
2 weeks agoon
July 10, 2024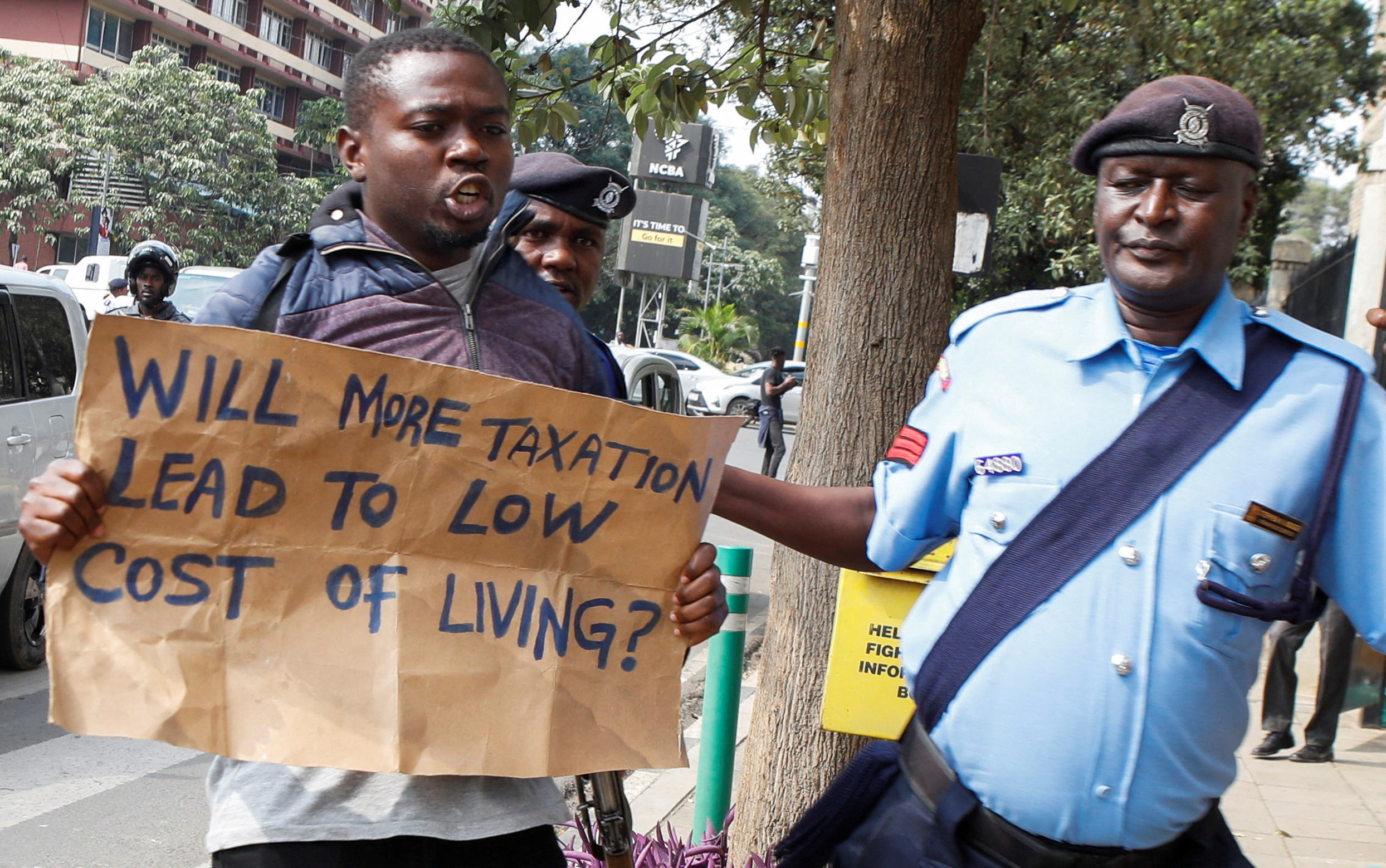
The surging crisis that is being witnessed in Kenya could end up being a good thing for Africa if the regional leaders could step back and examine the situation clinically with cool-headed interest. Maybe there is a hand of God in the whole affair. For, how do explain the flare not having started in harder-pressed countries such as Zambia, Mozambique and Ghana?
As fate would have it, it happened in East Africa, the region that is supposed to provide the next leadership of the African Union Commission, in a process that is about to start. And, what is the most serious crisis looming on Africa’s horizon? It is Debt of course.
Even the UN has warned the entire world that Africa’s debt situation is now a crisis. As at now, three or four countries are not facing debt trouble — and that is only for now.
There is one country, though, that is virtually debt-free, having just been freed from debt due to circumstances: Somalia. And it is the newest member of the East African Community. Somalia has recently had virtually all its foreign debt written off in recognition of the challenges it has been facing in nearly four decades.
Why is this important? Because debt is the choicest weapon of neocolonialists. There is no sweeter way to steal wealth than to have its owners deliver it to you, begging you, on all fours, to take it away from them, as you quietly thank the devil, who has impaired their judgement to think that you are their saviour.
So?
So, the economic integration Africa has embarked on will, over the next five or so years, go through are a make-or-break stage, and it must be led by a member that is debt-free. For, there is no surer weapon to subjugate and control a society than through debt.
A government or a country’s political leadership can talk tough and big until their creditor whispers something then the lion suddenly becomes a sheep. Positions agreed on earlier with comrades are sheepishly abandoned. Scheduled official trips get inexplicably cancelled.
Debt is that bad. In African capitals, presidents have received calls from Washington, Paris or London to cancel trips and they did, so because of debt vulnerability.
In our villages, men have lost wives to guys they hate most because of debt. At the state level, governments have lost command over their own institutions because of debt. The management of Africa’s economic transition, as may be agreed upon jointly by the continental leaders, needs to be implemented by a member without crippling foreign debt so they do not get instructions from elsewhere.
The other related threat to African states is armed conflict, often internal and not interstate. Somalia has been going through this for decades and it is to the credit of African intervention that statehood was restored to the country.
This is the biggest prize Africa has won since it defeated colonialism in (mostly) the 1960s decade. The product is the new Somalia and, to restore all other countries’ hope, the newly restored state should play a lead role in spreading stability and confidence across Africa.
One day, South Sudan, too, should qualify to play a lead role on the continent.
What has been happening in Kenya can happen in any other African country. And it can be worse. We have seen once promising countries with strong economies and armies, such as Libya, being ravaged into near-Stone Age in a very short time. Angry, youthful energy can be destructive, and opportunistic neocolonialists can make it inadvertently facilitate their intentions.
Containing prolonged or repetitive civil uprisings can be economically draining, both directly in deploying security forces and also by paralysing economic activity.
African countries also need to become one another’s economic insurance. By jointly managing trade routes with their transport infrastructure, energy sources and electricity distribution grids, and generally pursuing coordinated industrialisation strategies in observance of regional and national comparative advantages, they will sooner than later reduce insecurity, even as the borders remain porous.
EDITOR’S PICK


Trevor Noah set for ‘Off the Record’ world tour
South African comedian and talk show host, Trevor Noah, has announced a date for his “Off The Record” global tour...


SA mobility startup LULA acquires UK-based Zeelo’s operations
South Africa’s mobility startup, LULA, has announced the acquisition of the operations of UK-based Zeelo in a move that will...


Ngannou accuses Joshua of employing dirty tactics in their fight in Saudi Arabia
Former UFC heavyweight champion, Francis Ngannou, has accused British-Nigerian boxer, Anthony Joshua, and his promotion team of employing unfair and...


#EndBadGovernance Protests: Please be patient with Tinubu’s govt, monarchs beg Nigerian youths
Some prominent traditional rulers in Nigeria have pleaded with Nigerian youths and organizers of the planned nationwide #EndBadGovernance protests scheduled...


UNESCO removes Senegal’s Niokolo-Koba National Park from list of World Heritage sites in danger
The United Nations’ Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) has removed Senegal’s Niokolo-Koba National Park from the list of World...


At Project Aliyense discourse, panelists call for balance between free speech, ethical considerations
The government has been urged to balance freedom of speech with ethical considerations and laws that prevent harm to others....


Adenia Partners acquires Air Liquide’s operations in 12 African countries
Adenia Partners, a leading private equity firm, has completed the acquisition of Air Liquide’s operations in 12 African countries, adopting...


We will handle planned nationwide protests as family matter— Nigerian Govt
The Nigerian government says it will handle the planned #EndBadGovernance protests scheduled to commence on August 1 as a family...


Veteran Nigerian entertainer Charly Boy vows to divorce wife if Kamala Harris doesn’t win US presidential election
Veteran Nigerian entertainer, Charles Oputa, popularly known as Charly Boy, has vowed to divorce his wife of 47 years if...


Saudi club Al Hilal places African transfer record bid for Osimhen
Saudi Arabia club side, Al-Hilal, have reportedly made an African transfer record bid for Super Eagles and Napoli striker, Victor...
Trending
-

 Sports1 day ago
Sports1 day agoMeet Nigerian-born players doing big things for Japan at Paris 2024 Olympics
-

 Metro2 days ago
Metro2 days agoWe will handle planned nationwide protests as family matter— Nigerian Govt
-

 Metro15 hours ago
Metro15 hours ago#EndBadGovernance Protests: Please be patient with Tinubu’s govt, monarchs beg Nigerian youths
-

 Tech2 days ago
Tech2 days agoAdenia Partners acquires Air Liquide’s operations in 12 African countries


