Metro
Zambia’s digital economy: Balancing innovation, regulation
Published
5 months agoon
By
Isaac Dachen
Digital technologies are increasingly recognised as crucial tools for developing countries to accelerate economic growth and sustainable development.
These technologies can enhance service delivery, create new jobs and wealth, improve accountability and transparency, and support evidence-based policy-making, ultimately boosting productivity and growth.
The rapid evolution of new and emerging technologies is influencing economic activities in profound ways, making the landscape both dynamic and complex.
Zambia, with its youthful population, shows a strong appetite for digital technologies across various sectors of the economy.
According to the Zambia Statistics Agency (ZamStats), 48 percent of the population is under 14 years old, while only 3 percent are over 65.
Additionally, the 2021 World Development Index reported a youth unemployment rate of 26.1 percent, highlighting the urgent need for new opportunities to spur job creation across all sectors.
“Multiple assessments have revealed that Zambia has the necessary foundational elements to build a cohesive and integrated digital economy that unlocks several financial and economic opportunities for its citizens,” stated a report on Zambia’s digital economy.
The 2020 World Bank Digital Economy Diagnostic report acknowledged key advancements, such as the expansion of Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) network coverage, the deployment of a backbone fibre network, increased uptake of digital financial services, and the digitalization of government services.
However, it also noted gaps in the policy, legal, and regulatory environment, as well as in digital skills and the innovation and entrepreneurship ecosystem.
A 2021 analysis by the Zambian government and the United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF) echoed these findings, emphasizing that while Zambia possesses the necessary elements for building a digital economy, a more targeted approach is required to fully realize the benefits.
The report highlighted the need for enhanced coordination on policy and regulatory issues, increased investments in infrastructure, and the development of basic, intermediate, and advanced digital skills.
Digital platforms and services in Zambia are emerging across various sectors, such as Smartcare for patient records management in health, digital platforms in agriculture, and significant adoption of mobile money services in the financial sector.
Progress has also been made in digitalizing tax collection processes by the Zambia Revenue Authority (ZRA), marking a key milestone in the country’s journey towards a digital economy.
However, there is still work to be done to develop digital platforms in sectors like tourism, agriculture, and transportation, and to create linkages between existing services for a more integrated digital economy.
Enhancing the performance of existing digital platforms and expanding their reach across various sectors remain critical steps.
Investing in these areas could greatly increase efficiencies in both the public and private sectors by leveraging the potential of digital technologies.
Moreover, unlocking new opportunities in the digital economy for innovators, start-ups, and content creators can significantly contribute to overall economic growth in Zambia.
Zambia stands at a pivotal moment, where balancing innovation with effective regulation could unlock substantial benefits for its economy and citizens, driving the nation towards a more digitally inclusive future.
This story is sponsored by Project Aliyense.
You may like
-


Zambia announces second case of Mpox as country battles cholera outbreak
-


Zambian NGOs rate President Hichilema’s reforms as not far-reaching
-


Zambian drug agency declares ex-President Lungu’s daughter wanted
-


Zambian NGO decries persistent corruption, says governance in 2024 marked by mixed fortunes
-


Zambia: Expert warns of food security threat due to climate change
-


Swiss company Mercuria partners Zambia’s IDC in new metals trading firm
Metro
‘Don’t start what you can’t finish’, ex-Nigerian official replies President Tchiani
Published
3 weeks agoon
December 29, 2024
Former Nigerian Aviation Minister, Femi Fani-Kayode, has told President Abdourahamane Tchiani of Niger Republic to refrain from making infantile and puerile allegations that Nigeria is conniving with France and the Lakurawa terrorists to destabilize his country.
Tchiani had, during an interview with Radio-Télévision du Niger on December 25, accused the Nigerian government of using the sect, with the help of foreign security forces notably from France, to wreck havoc in his country, insinuating that President Bola Tinubu had been paid by the France government to allow their military to establish a base in Borno State.
He also alleged that Nigeria, acting in collaboration with the French government and the terrorist group, was responsible for an attack on the Niger-Benin oil pipeline on December 13, 2024, in Gaya, Dosso Region of Niger Republic.
But in a statement he posted on his official X handle on Sunday, Fani-Kayode who is popularly called FFK, said Nigeria does not need the help of France and thr Lakurawa terrorist to destabilize Niger Republic.
FFK insisted that Nigeria is not part of the western powers sponsoring terrorists organizations to wretch havoc on the West African sub region.
“If Nigeria wanted to destabilise Niger Republic, I do not believe that we would need France or any terrorist organisation to do so,” the politician wrote.
He noted that on the contrary, western powers are the ones behind terrorist organizations operating in the region and other parts of Africa.
“I have maintained that the western powers are behind the terrorist groups that have plagued the West African sub region over the last 15 years and for the last ten years I have publicly stated this and given my reasons.
“I am equally certain that Nigeria, being one of the major victims of these terrorist organisations, has had no part in it and that no Nigerian President, past or present, has indulged in such grave and dangerous actions.”
He went on to advice Tchiani against provoking Nigeria with unguarded and infantile utterances capable of stoking Nigeria against his country.
“The Nigerien Military Head of State, Abdourahamane Tchiani, would do well to be careful not to provoke our wrath with his absurd assertions and remain mindful of the fact that the defence budget for his country, Mali and Burkina Faso COMBINED is not up to 25% of Nigeria’s.
“Tchiani’s grave allegations that President Tinubu and NSA Nuhu Ribadu have been bought by the French to destabilise Niger Republic, that our Government is jointly sponsoring a terrorist group with France to do same and that there are French military bases in Nigeria are infantile, puerile, mendacious and asinine.
“It is a squalid attempt by the Nigerien Head of State to sow the seeds of dissention in our country, to alienate our people from constituted authority, to divide our people and to undermine the Tinubu administration,” he added.
“It is also highly provocative and the FG should consider the possibility of taking other more extreeme measures if this reckless provocation continues.
“We are under no obligation to show restraint when we are being undermined and maligned.
Metro
Zambia announces second case of Mpox as country battles cholera outbreak
Published
4 weeks agoon
December 28, 2024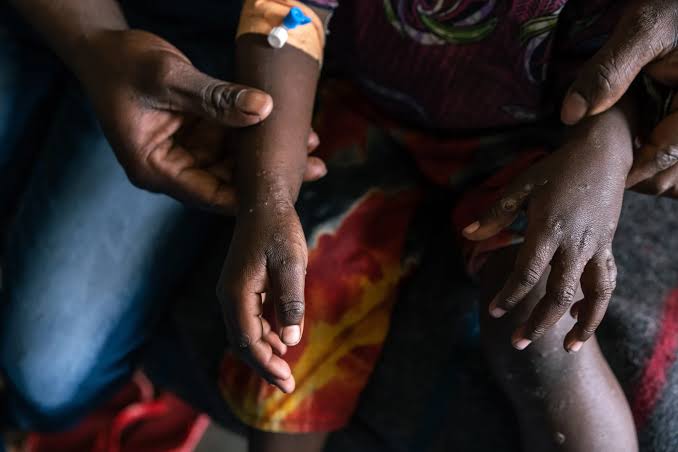
The Zambian Ministry of Health has reported a second case of Monkeypox, popularly known as Mpox, in Kitwe region of Copperbelt Province.
Acting Health Minister, Douglas Syakalima, who made the announcement on Friday during a press conference in Lusaka, revealed that the Ministry is intensifying contact tracing and surveillance to curb further spread of the disease.
Syakalima who also addressed the ongoing cholera outbreak in Nakonde, Muchinga Province, said thus far, seven cases have been confirmed.
“The second Mpox case involves a 34-year-old female from Ndeke, Kitwe, who presented with symptoms including rash, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and oral ulcers on December 21,” Syakalima said at the press parley.
He noted that there was an initial misdiagnosis with chickenpox in Lumwana, North-Western Province, but laboratory tests on December 26 confirmed that it was Mpox.
Syakalima added that the patient’s husband, who works in a neighboring country with confirmed Mpox cases, had experienced similar symptoms earlier this month.
“Both patients are now stable and under close monitoring. A rapid response team has been deployed to trace contacts and prevent further spread,” he said, adding that eight close contacts of the couple are currently under observation, while nationwide surveillance has been heightened.
The Health Minister added that on December 26, five cholera cases were confirmed at Nakonde Urban Clinic with the first three patients, a husband, wife, and their son, admitted on December 24 with symptoms of diarrhea, vomiting, dehydration, and shock.
“Today, two more cases have been reported, bringing the total to seven confirmed cholera cases from the same household,” Syakalima stated.
He explained that Nakonde’s location as a border town with high cross-border movement poses a risk for the disease to spread to other parts of the country.
The Minister however, assured that the Ministry has deployed teams to trace contacts, chlorinate water sources, disinfect affected homes, and activate Incident Management Systems at district and provincial levels while surveillance has been heightened, and contact tracing is ongoing for 33 individuals.
“The government remains committed to preventing further spread of these diseases,” Syakalima assured.
EDITOR’S PICK


Nigeria: Marketers predict further price cut as another refinery begins operations
Oil marketers and the Nigerian Midstream and Downstream Petroleum Regulatory Authority expect refined petroleum product prices to reduce as another...


Kenya: Consumer inflation rises to 3.0% from 2.8%
Kenya’s statistics agency said on Tuesday that Kenya’s consumer price inflation increased slightly to 3.0% year-over-year in December from 2.8%...


South Africa’s Transnet’s half-year deficit hits $117m
Transnet, a state-owned logistics company in South Africa, announced on Tuesday that it had lost 2.2 billion rand ($117.48 million)...


Nigeria, China extend $2bn currency swap deal
A 15 billion yuan ($2 billion) currency-swap arrangement between China and Nigeria has been extended to boost investment and commerce...


Egypt’s central bank maintains overnight rates
As anticipated, Egypt’s central bank has maintained its overnight interest rates, stating that although inflation was predicted to drop significantly...


Illicit flows cost Nigeria, others $1.6bn daily— AfDB
According to the African Development Bank (AfDB), illicit money flows and profit shifting by multinational corporations doing business in Africa...


‘Don’t start what you can’t finish’, ex-Nigerian official replies President Tchiani
Former Nigerian Aviation Minister, Femi Fani-Kayode, has told President Abdourahamane Tchiani of Niger Republic to refrain from making infantile and...


Again, Starlink raises prices of its services in Nigeria
Elon Musk’s satellite internet service provider, Starlink, has again jacked up the prices of its services in Nigeria after an...


Former President of Moroccan club Raja sentenced to 3 years in prison
The former President of Moroccan top club, Raja Casablanca, Mohamed Aouzal, has been sentenced to three and a half years...


Zambia announces second case of Mpox as country battles cholera outbreak
The Zambian Ministry of Health has reported a second case of Monkeypox, popularly known as Mpox, in Kitwe region of...


